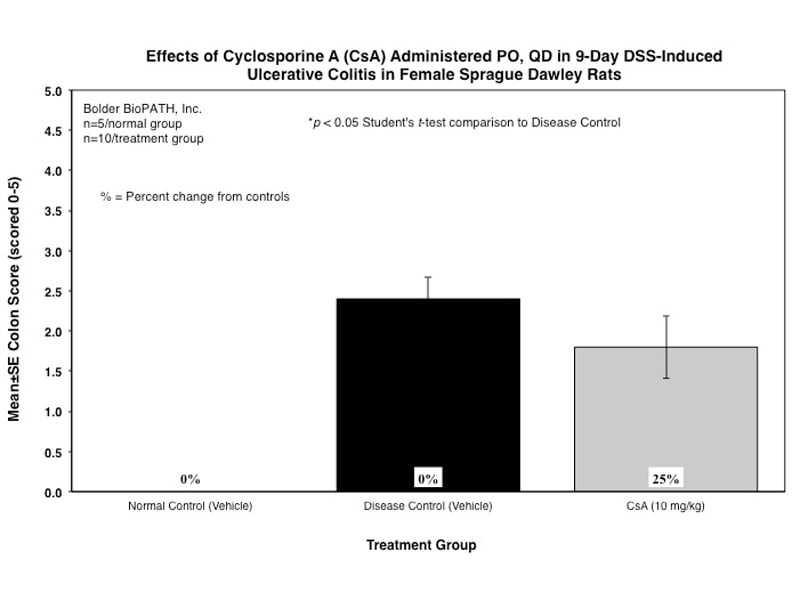
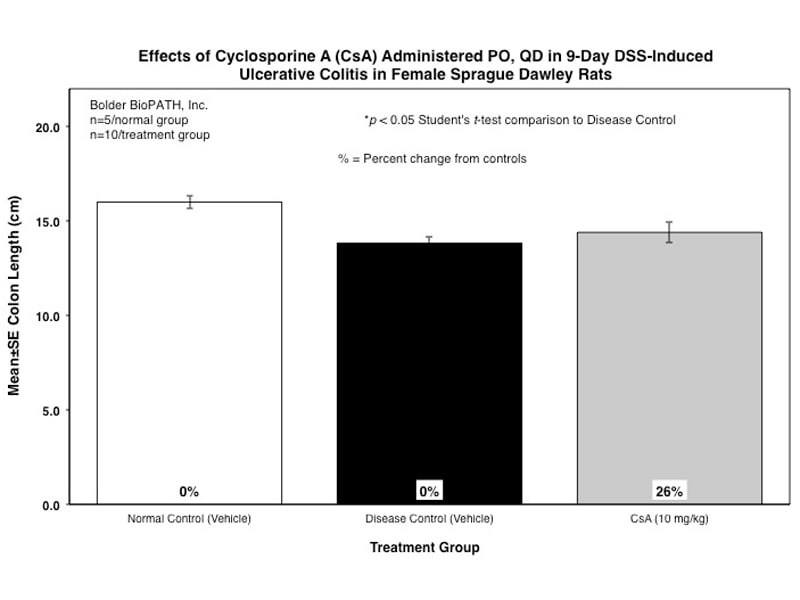
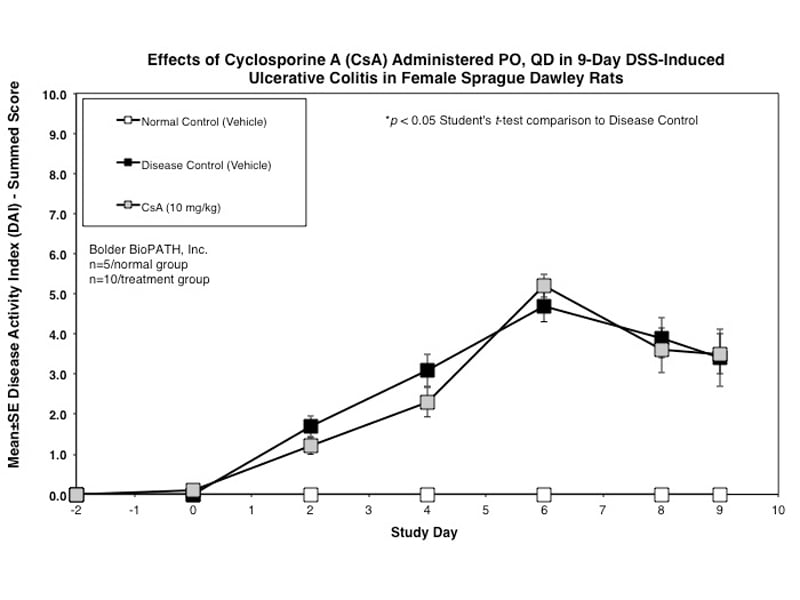
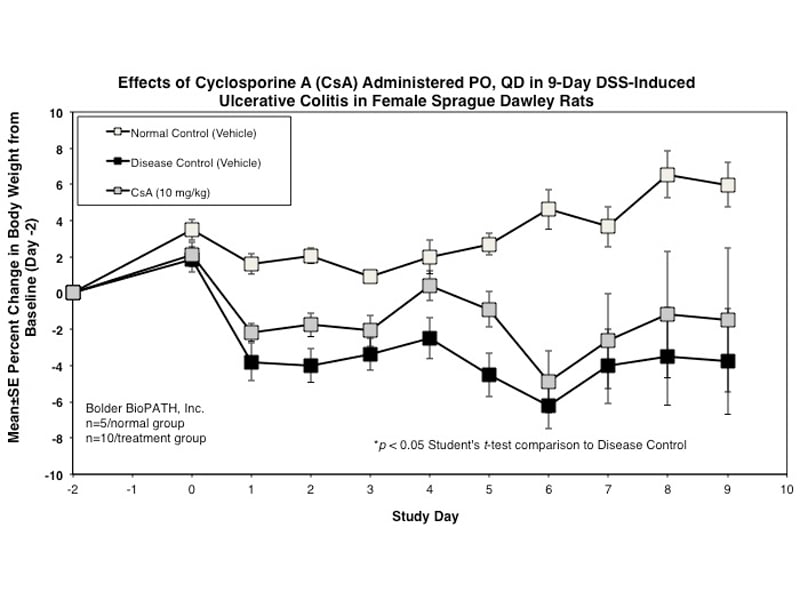
Dextran Sulfate Salt Induced Colitis (DSS) in Rat

Induction:
Rats are exposed to Dextran Sulfate Salt (DSS) in water for 5 to 7 days to induce inflammation and gland loss with erosion in the colon.
Disease Parameters:
Rats have been shown to develop acute colitis with signs of diarrhea, gross rectal bleeding, and body weight loss within 6 to 10 days after ingesting DSS. Gross and histopathologic changes resulting from this treatment resemble somewhat those occurring in human ulcerative colitis, a subset of inflammatory bowel disease.1–5
Dosing Paradigms:
- Dosing is initiated prior to or once exposure to DSS begins and continues until study termination.
- Route of administration: SC, PO, IP, IV, IC
Clinical Assessment:
Rats are weighed and water consumption is measured daily. Disease Activity Index is scored every other day using the following criteria:
Weight Loss (%):
0 = ≤ 2%
1 = 3 to 6%
2 = 7 to 12%
3 = > 12%
Stool Consistency:
0 = Normal Stool (well-formed pellets)
1 = Semi-solid Stool
2 = Loose to Pasty Stool (does not adhere to the anus)
3 = Diarrhea (liquid stool that adhered to the anus)
ccult/Gross Blood (Using Hemoccult Test):
0 = Normal
1 = Positive Test
2 = Gross Blood in Stool
3 = Rectal Bleeding
At necropsy, the entire colon is harvested from each rat and assessed for evidence of blood or blood-tinged fluid for evaluation of colon content scores. Colon content is scored according to the following criteria:
Gross Scoring Criteria:
0 = Normal, no blood observed
1 = Semi-solid stool
2 = Semi-solid stool, may be slightly blood tinged
3 = Fluid stool with definite evidence of blood
4 = Bloody fluid
5 = No content, (include animals with no observable distal content in this category)
Histopathological Assessment:
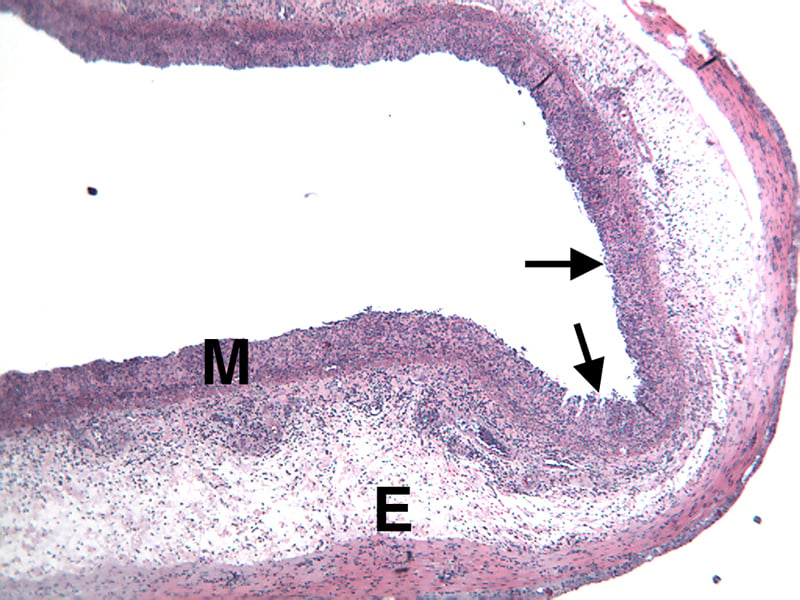
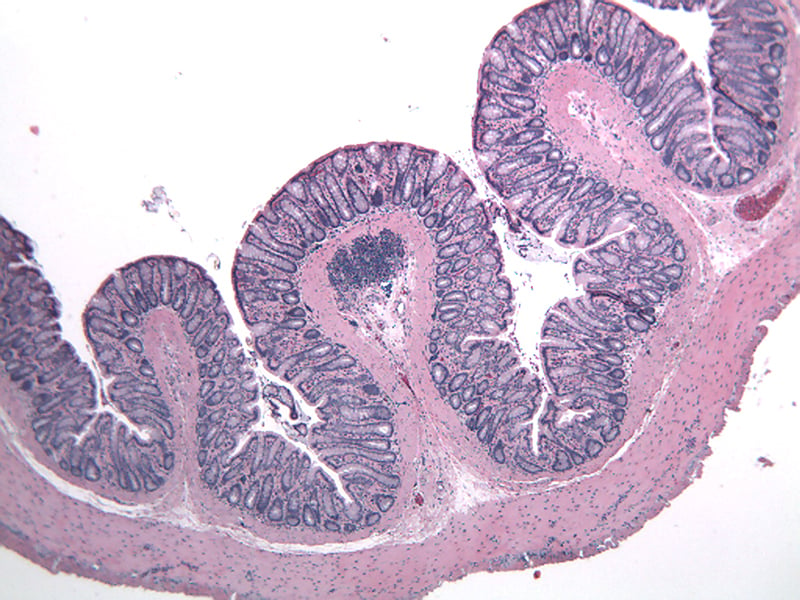
The colon is cut into Proximal and Distal halves and collected for processing and embedding. Each half is sectioned into 3 equidistant pieces and these sections are stained to quantitate inflammation, gland loss and epithelial loss (hematoxylin & eosin), which are scored according to these methods.
Sample Data (Click on image to enlarge):
Representative Photomicrographs of colons
For additional examples of positive controls, please contact us.
Notes:
Compounds that are effective in the treatment of human IBD have activity in this model and it is being used to investigate potential new therapies.
Optional Endpoint
- PK/PD blood collections
- Cytokine/chemokine analysis via Luminex(R)
- Other sandwich ELISAs
- CBC/clinical chemistry analysis
- Soft tissue collection
- Histopathologic analysis
- Immunohistochemistry analysis
- Disease Activity Index (DAI)
- Endoscopy
References
- Shi X, Winston JH, Sarna SK. Differential immune and genetic responses in rat models of Crohn’s colitis and ulcerative colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2011; 300:G41–G51.
- Strober W, Fuss IJ, Blumberg RS. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 2002; 20:495–549.
- Faure M, Mettraux C, Moennoz D, et al. Specific amino acids increase mucin synthesis and microbiota in dextran sulfate sodium-treated rats. J Nutr 2006; 136:1558–1564.
- Woodruff SA, Masterson JC, Fillon S, et al. Role of eosinophils in inflammatory bowel and gastrointestinal diseases. JPGN 2011; 52(6): 650–661.
- Arslan G, Erichsen K, Milde AM, et al. No protection against DSS-induced colitis by short-term pretreatment with seal or fish oils in rats. Integr Med Insights 2007; 2: 25–34.