Collagen Induced Arthritis (CIA) In Rat

Rat collagen induced arthritis (CIA) is an experimental model of polyarthritis that has been widely used for preclinical testing of numerous anti-arthritic agents, which are either under preclinical or clinical investigation, or are currently used as therapeutics in this disease.
Induction:
On study day 0 and day 7, female rats are given intradermal injections of bovine or porcine type II collagen
(1 to 2 mg/mL in incomplete Freund’s Adjuvant) at multiple sites on the lower back.
Disease Parameters:
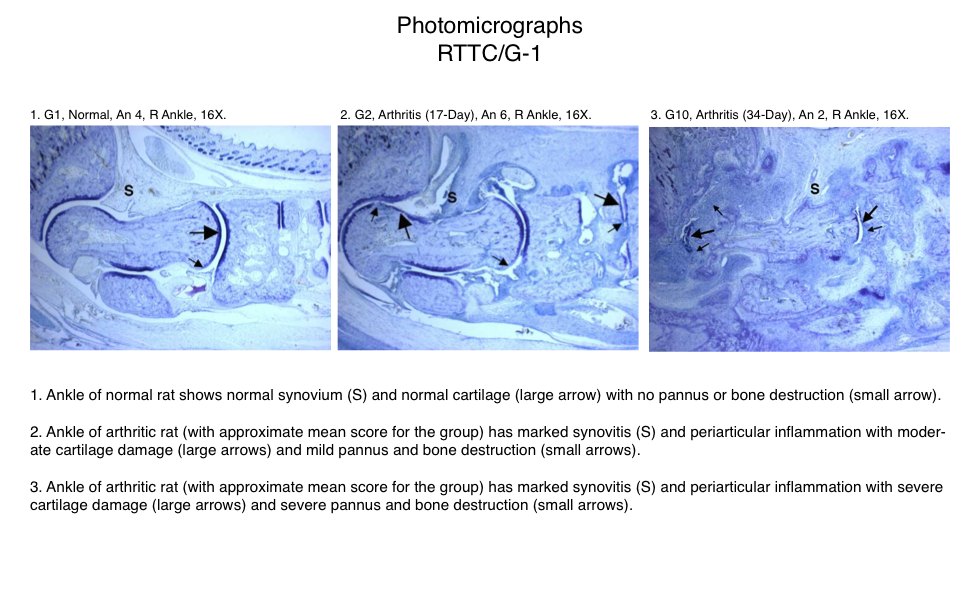
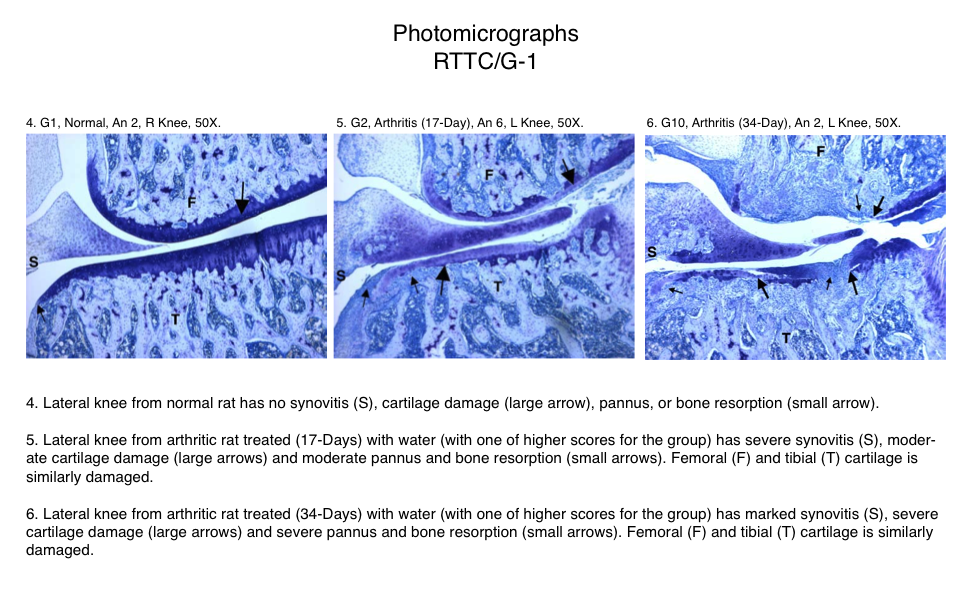
The resulting polyarthritis (occurring on or around day 11) is characterized by marked cartilage destruction associated with immune complex deposition on articular surfaces, bone resorption and periosteal proliferation, and moderate to marked synovitis and periarticular inflammation1,2,3. The lesions in type II collagen arthritis are somewhat more analogous to those seen in human RA than are the lesions of adjuvant arthritis in that there is more extensive pannus associated cartilage destruction. However, adjuvant arthritis has been used much more extensively for pharmaceutical testing and therefore more data exists for comparison in humans.
Dosing Paradigms:
- Developing (Prophylactic) – Begin dosing on study day 0 (or earlier) and continue until necropsy on day 17 (out to day 34).
- Semi-Established (Prophylactic) – Begin dosing on study day 6 or 9 and continue until necropsy on day 17 (out to day 34).
- Established (Therapeutic) – Begin dosing on study day 11 to 13 and continue until necropsy on day 17 (out to day 34).
- Route of administration: SC, PO, IP, IV
Clinical Assessment:
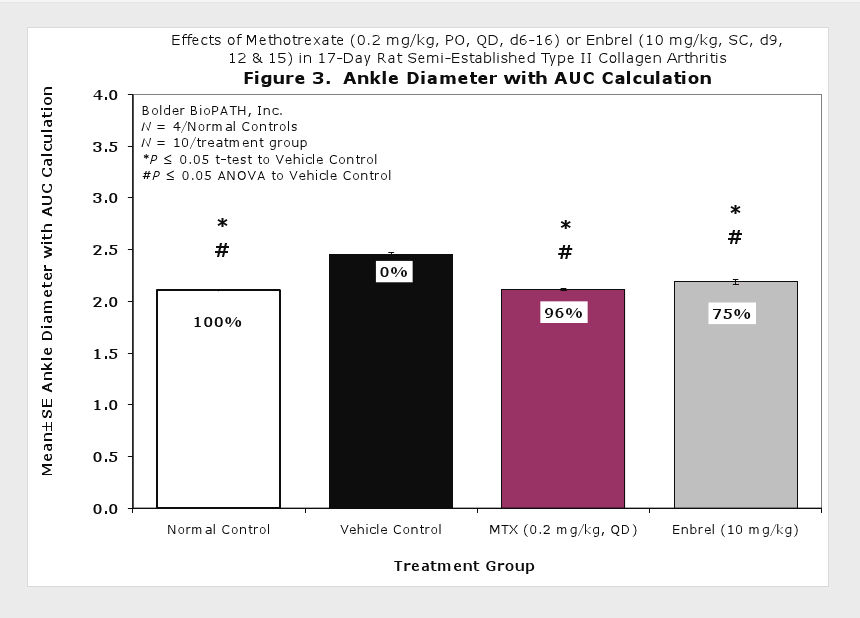
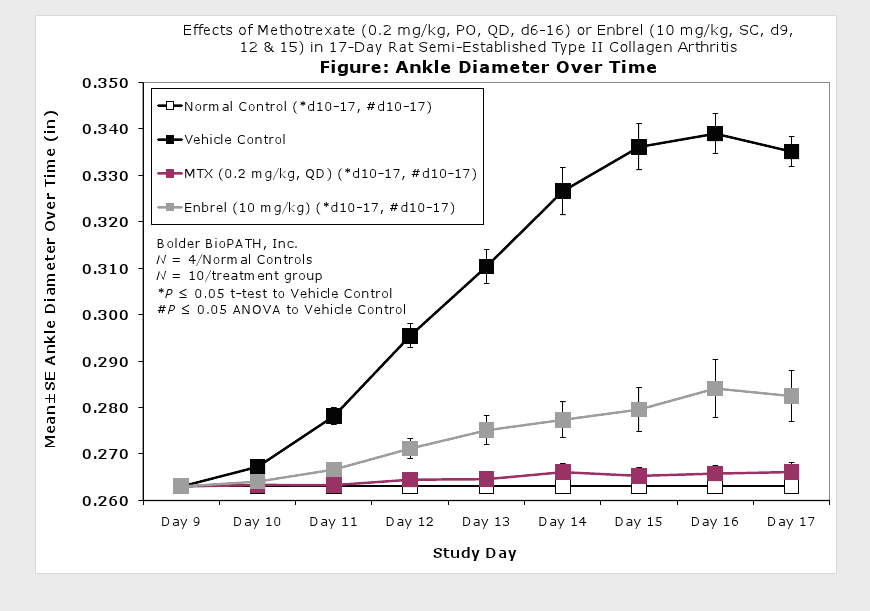
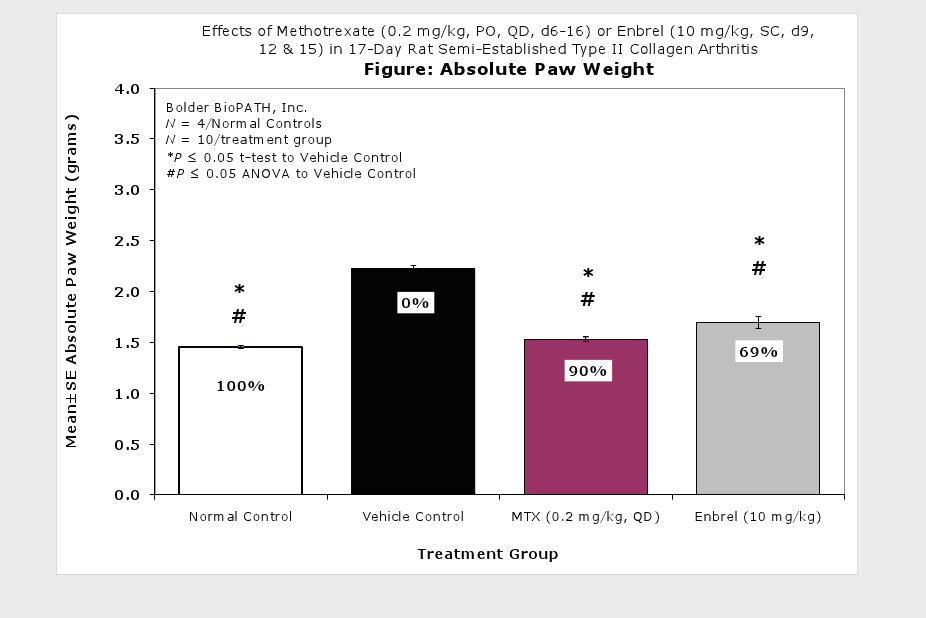
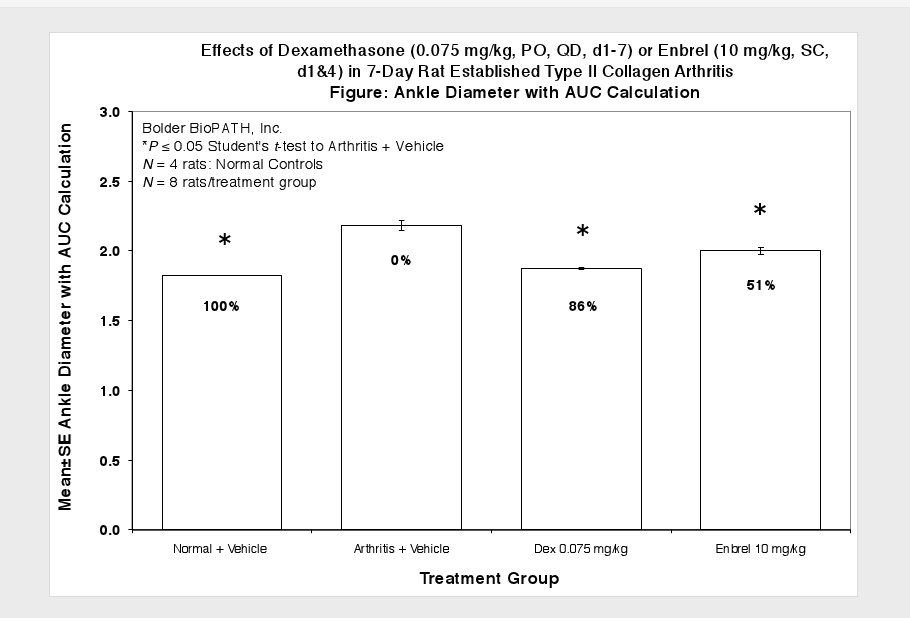
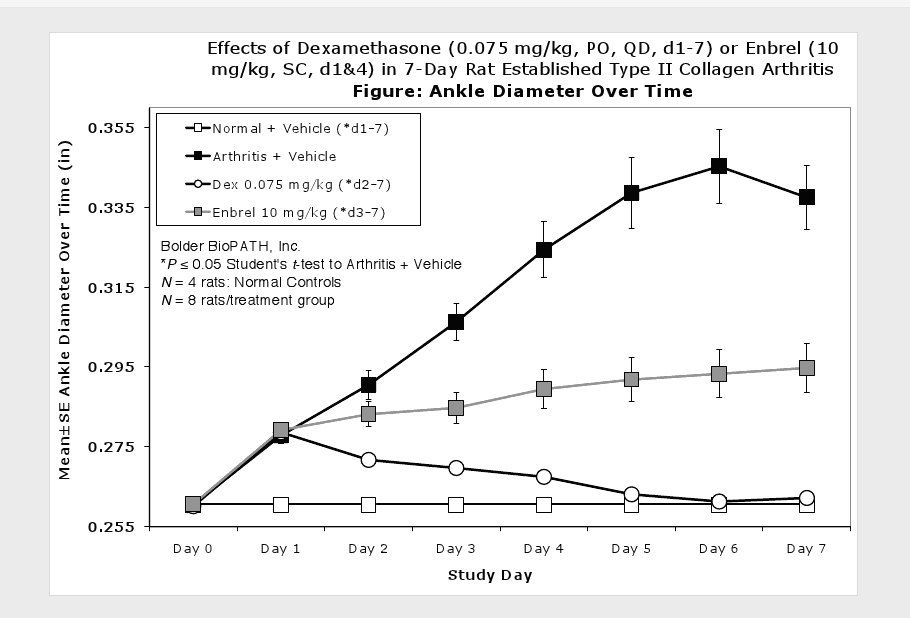
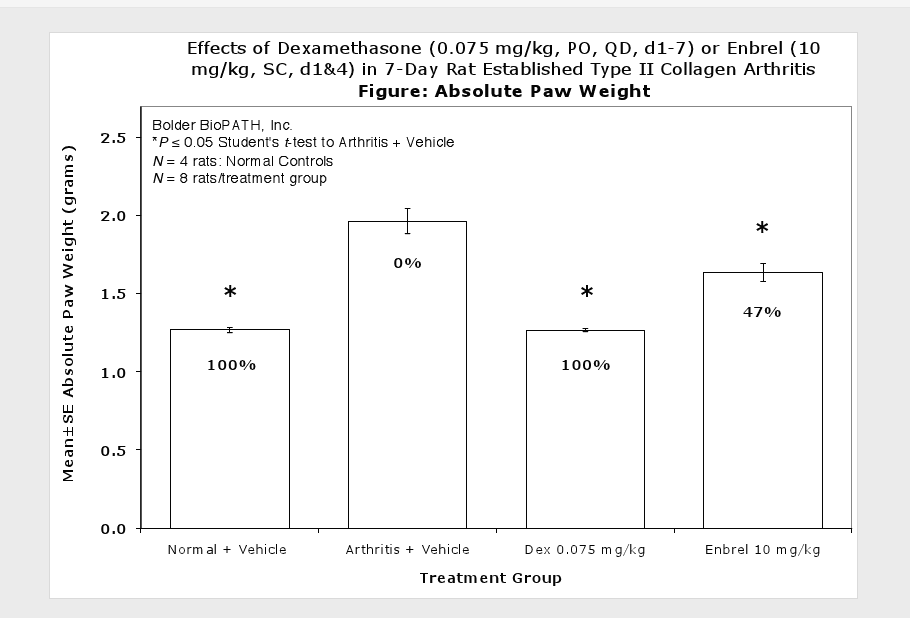
Caliper measurements of ankle joint width are done on study days 9 through termination. At termination, the tibiotarsal joint is transected at the level of the medial and lateral malleolus for determination of paw weights as another measure of inflammation.
Histopathological Assessment:
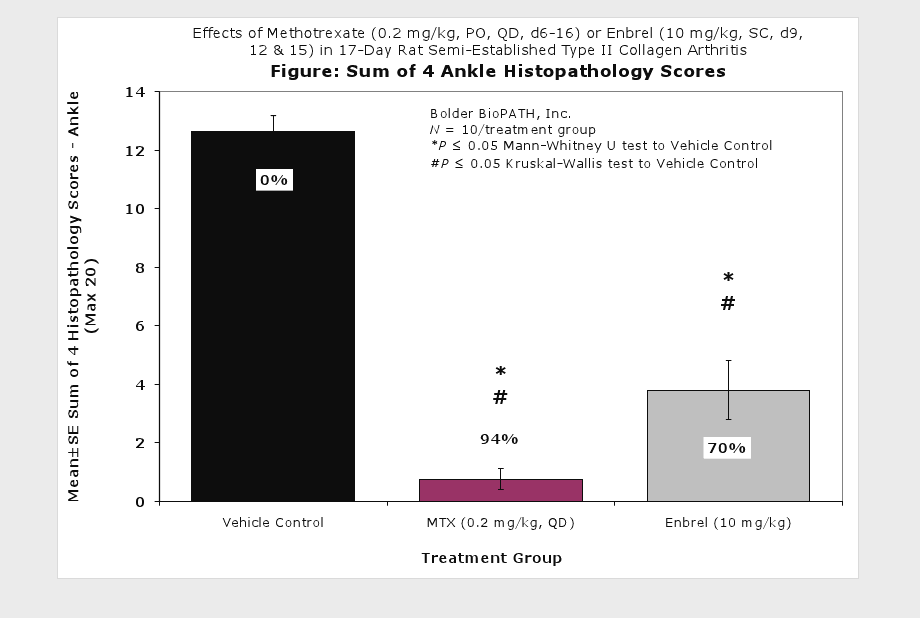
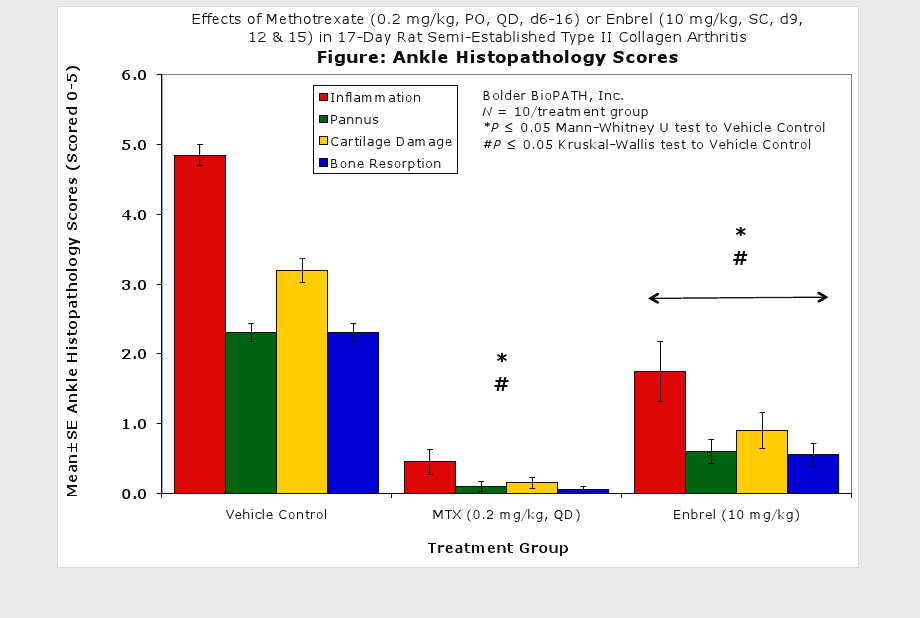
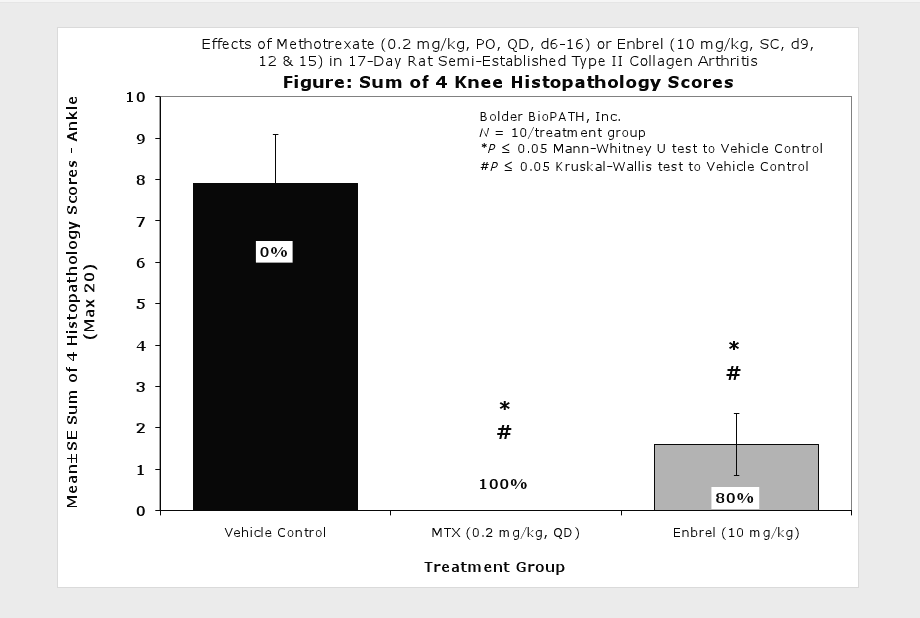
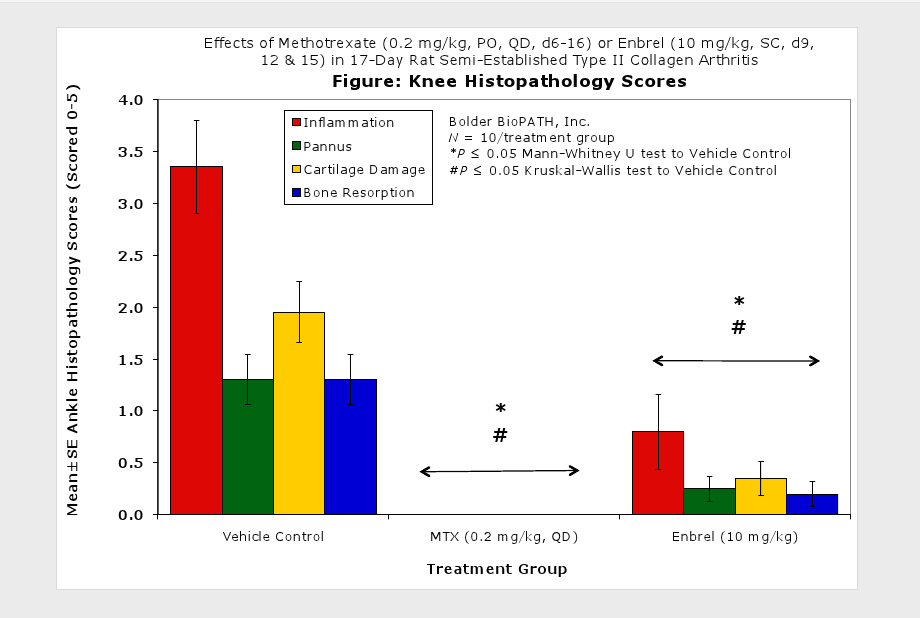
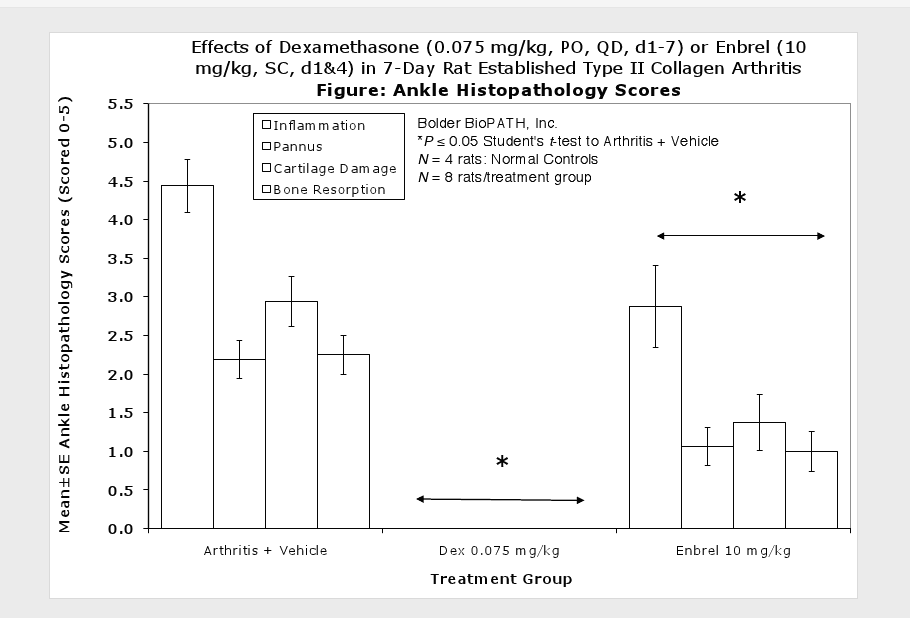
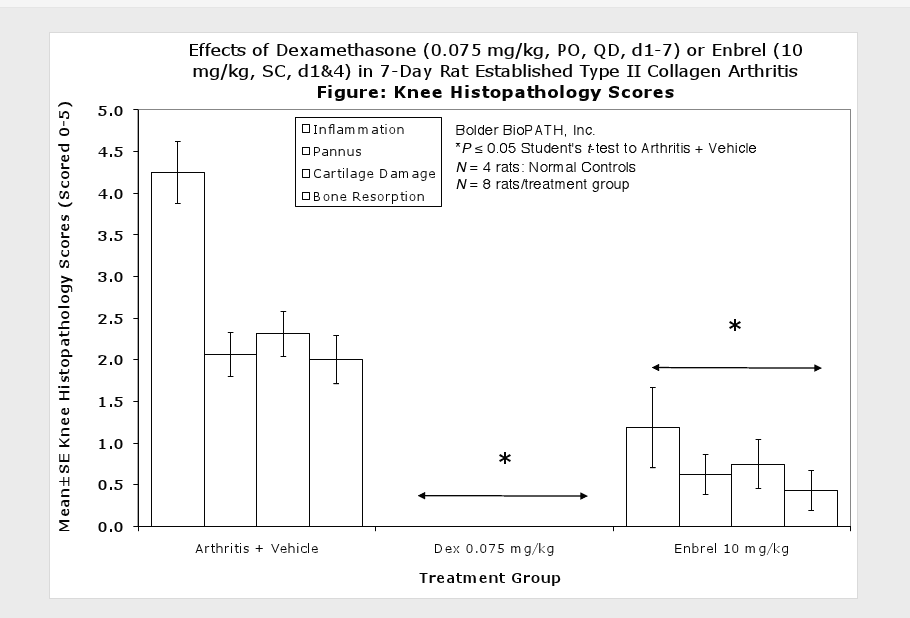
Fore paws, hind paws/ankles, and knees are given scores of 0 through 5 for inflammation, pannus formation, cartilage damage and bone resorption according to these methods.
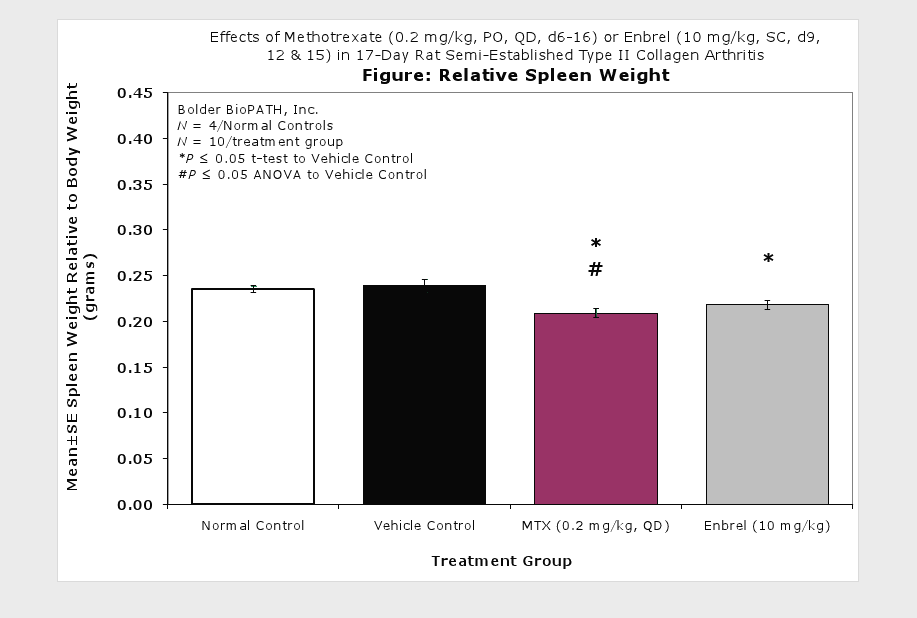
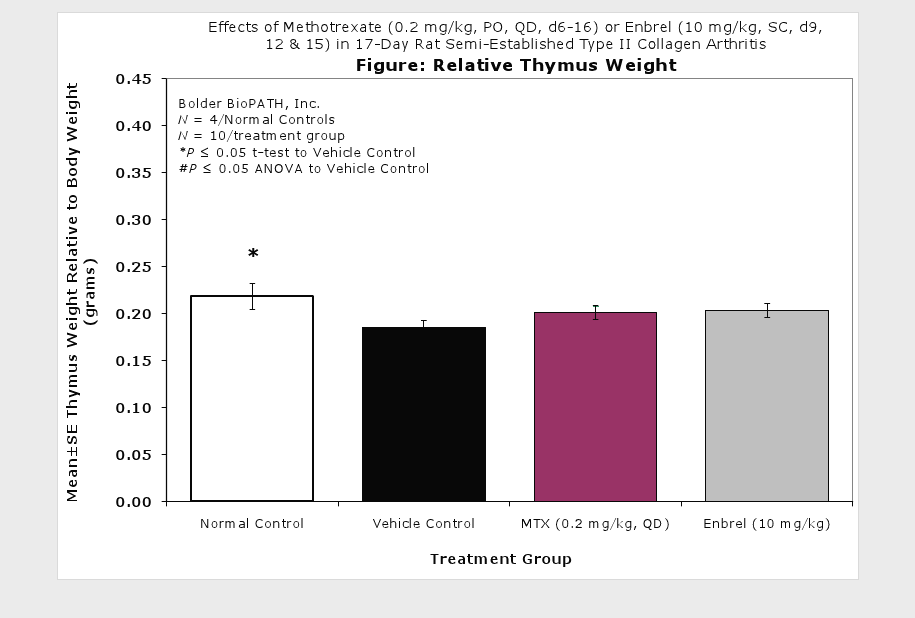
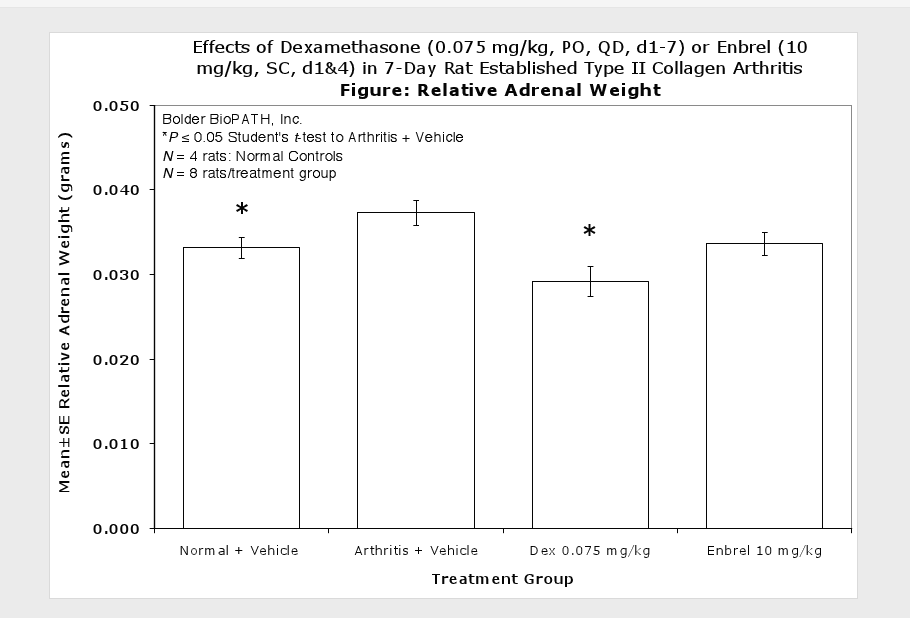
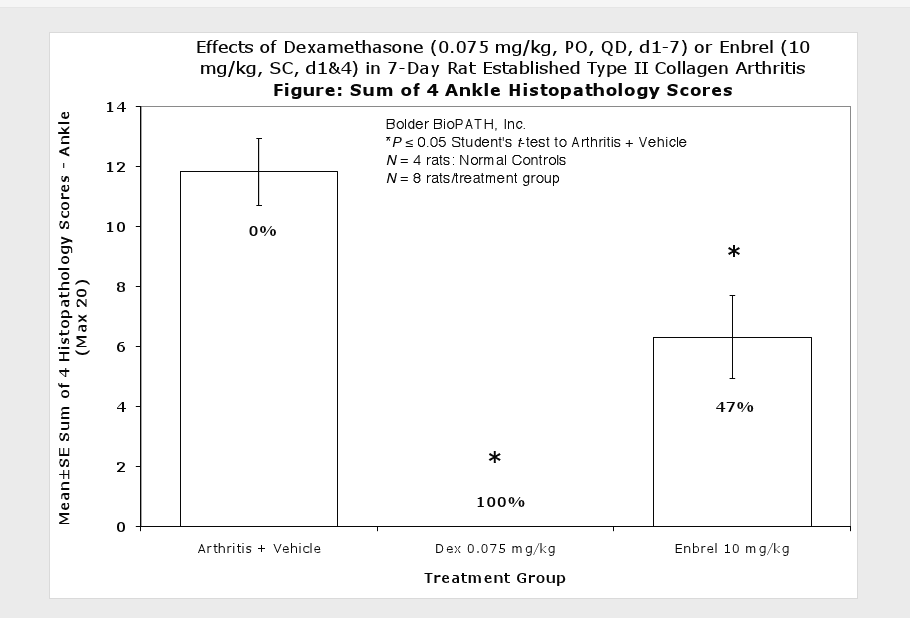
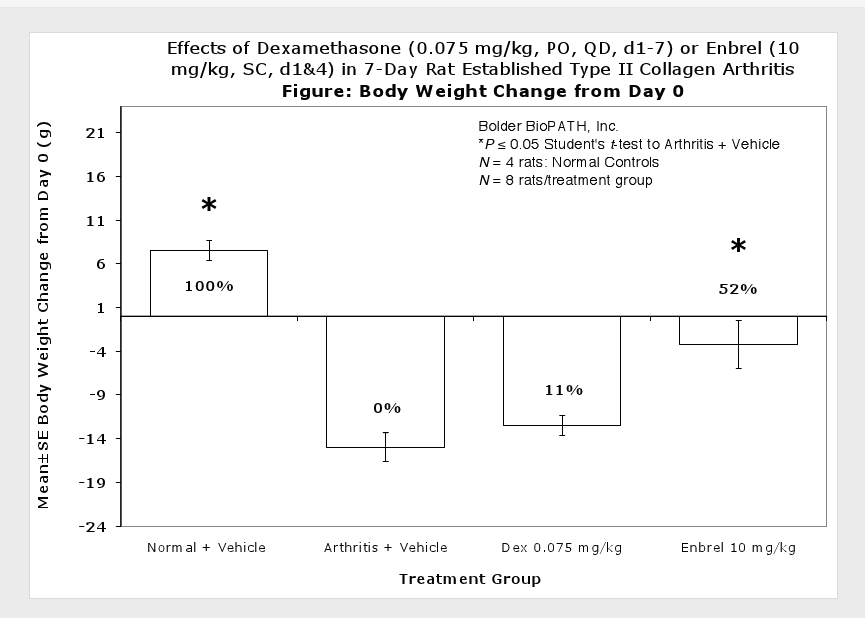
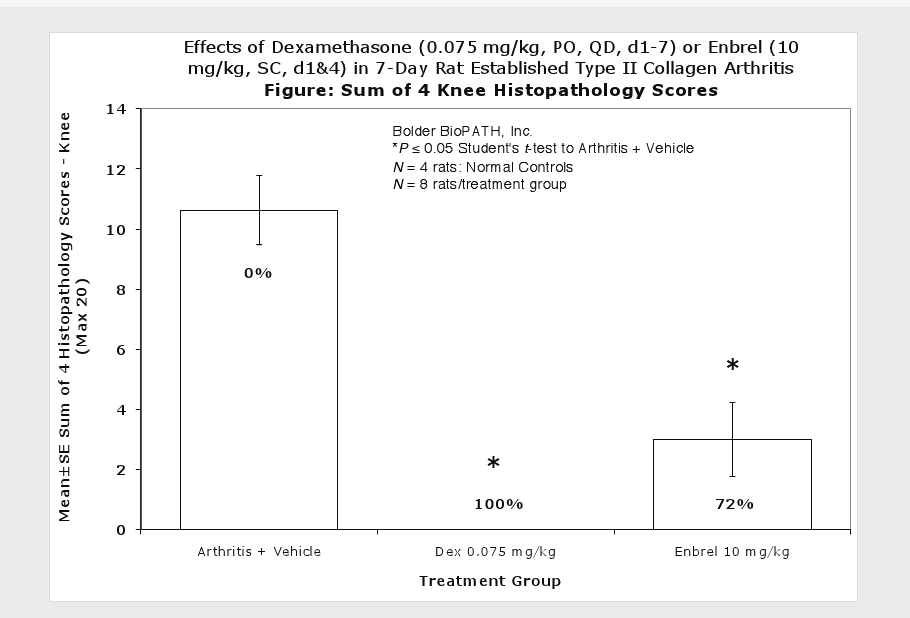
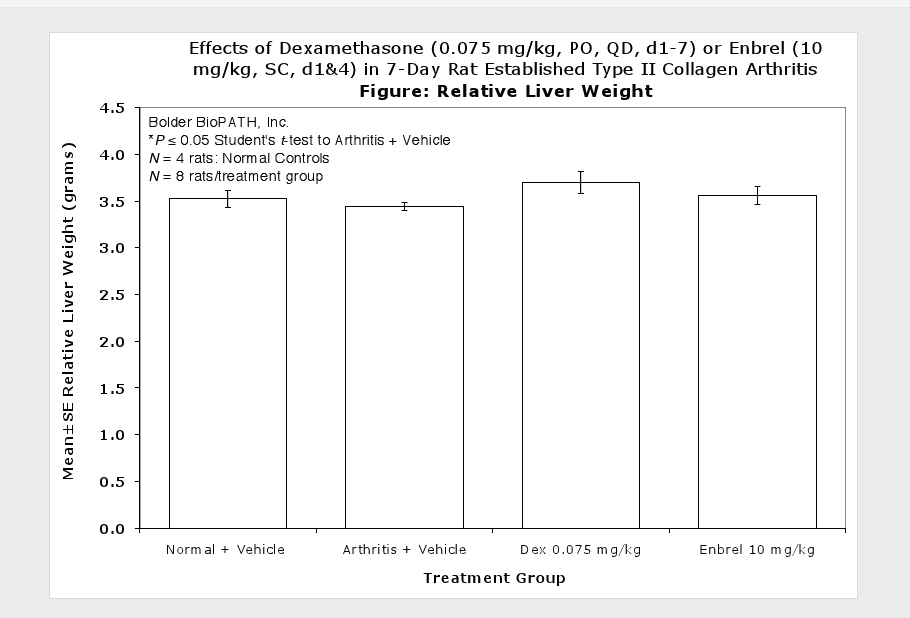
Sample Data (click on image to enlarge):
Representative Photomicrographs of Ankle/Knee Joints
(Normal, 17-Day Arthritis and 34-Day Arthritis)
Semi-Established Model
Established Model
For additional examples of positive controls, please contact us.
Notes:
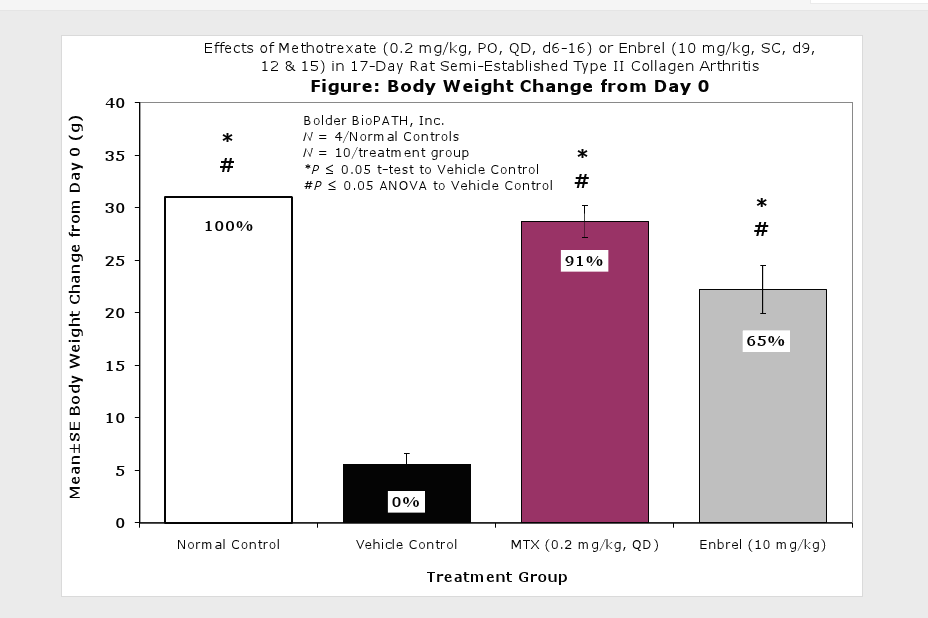
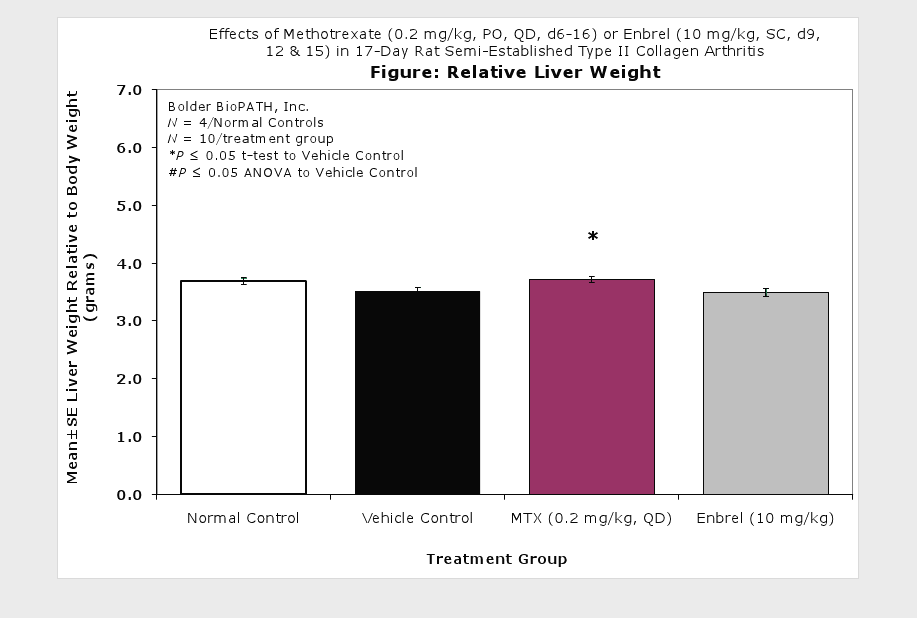
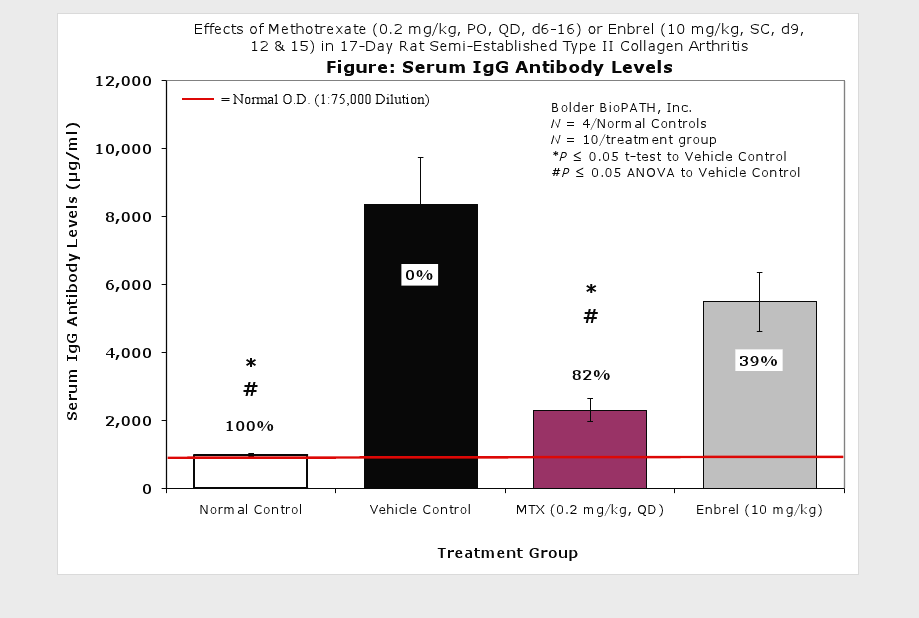
Clinically used agents that show activity in established collagen arthritis include corticosteroids, indomethacin and to a lesser extent, methotrexate4. Biological agents such as IL-1ra and the soluble TNF receptors are active in this test system and combination therapies with IL-1 ra and PEG sTNF-RI show potential for greater than additive effects5. Activity of commonly used small molecule anti-arthritic agents such as dexamethasone, indomethacin (and other NSAIDs including cyclo-oxygenase 2 inhibitors) and methotrexate eare predicted by the established rat type II collagen arthritis models.
Optional Endpoint:
- PK/PD blood collections
- Cytokine/chemokine analysis via Luminex(R)
- Other sandwich ELISAs
- CBC/clinical chemistry analysis
- Soft tissue collection
- Histopathologic analysis
- Immunohistochemistry analysis
References
- Terato, K., et al. (1992). Induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to collagen. J Immunol 148(7): 2103–2108.
- Nandakumar KS, Svensson L, Homdahl R (2003). Collagen Type II-Specific Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Mice. Am J Pathol 163(5): 1827–1837.
- Terato, K., et al. (1995). Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice: Synergistic Effect of E. Coli Lipopolysaccharide Bypasses Epitope Specificity in the Induction of Arthritis with Monoclonal Antibodies to Type II Collagen. Autoimmunity 22(3): 137–147.
Referenced Work:
- Chang, B, et al, The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 ameliorates autoimmune arthritis by inhibition of multiple effector cells
Arthritis Research & Therapy 2011 - Cowden, J. et al, The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and Th17 responses in preclinical models of arthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 2014
For more information about Antibody Induced Arthritis contact us here.