Antibody Induced Arthritis in Mouse (ManIA)

Overview of Antibody Induced Arthritis in Mouse
Antibody induced arthritis via monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to collagen have been shown to induce arthritis lesions in various strains of mice, with combinations of three or more antibodies resulting in severe arthritis with marked destruction of articular cartilage.
Induction:
On study day 0, mice are injected intravenously (IV) with 3 mg of monoclonal antibody (mAb). On day 3, mice are dosed intraperitoneally (IP) with E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (25 µg/mouse).
Disease Parameters:
Arthritis has been demonstrated to occur within 48 to 72 hours post-injection with antibodies, resulting in disease that persists for at least three weeks1, 2. E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a strong inducer of pro-inflammatory cytokines, acts synergistically in the induction of antibody-mediated arthritis, and negates the multiple epitope specificity of autoantibodies in the model3.
Dosing Paradigms:
Treatment is initiated approximately 1 to 2 hours prior to mAb injection (d0) and continues for 14 days (days 0 through 13).
Clinical Assessment:
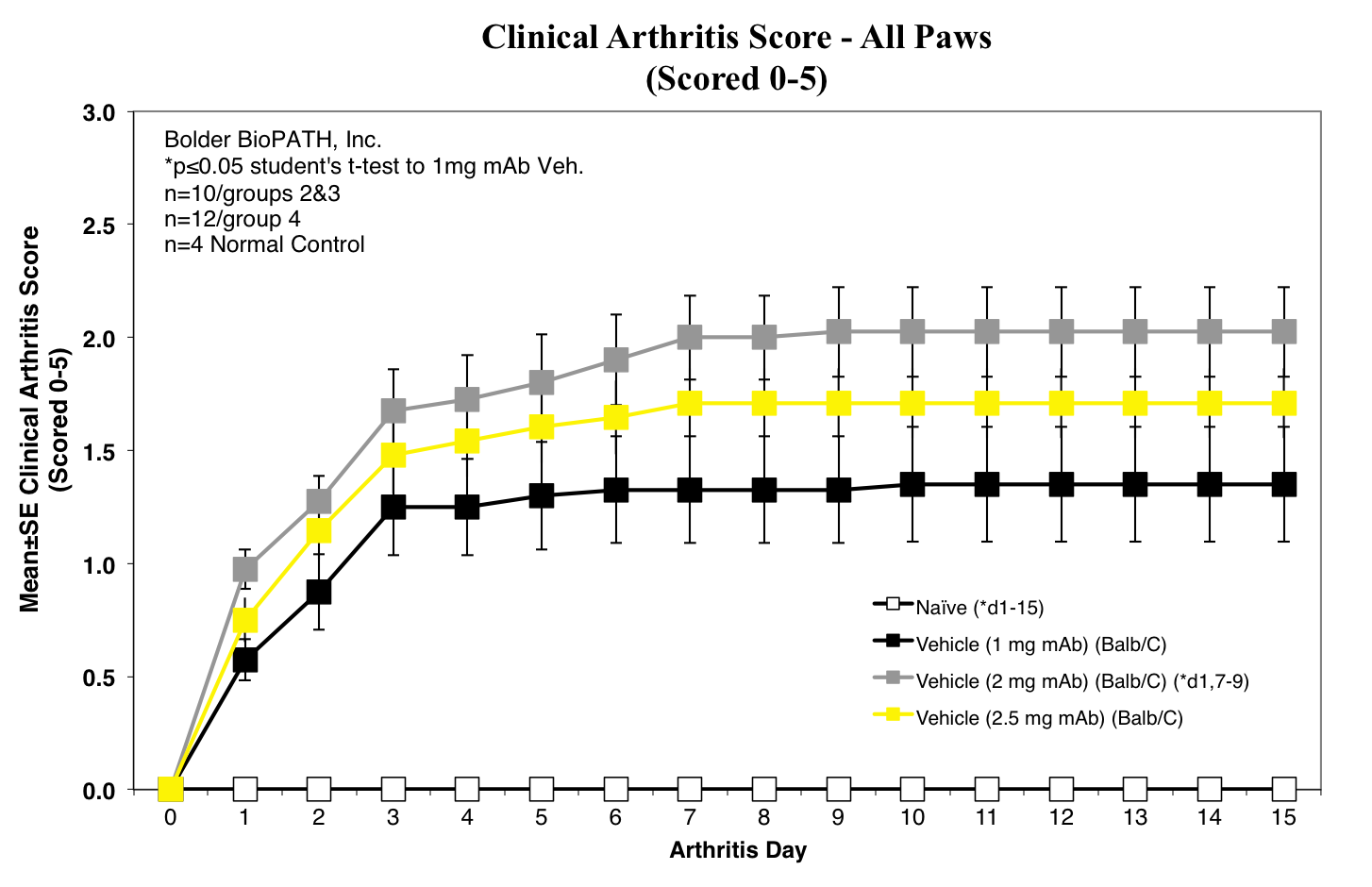
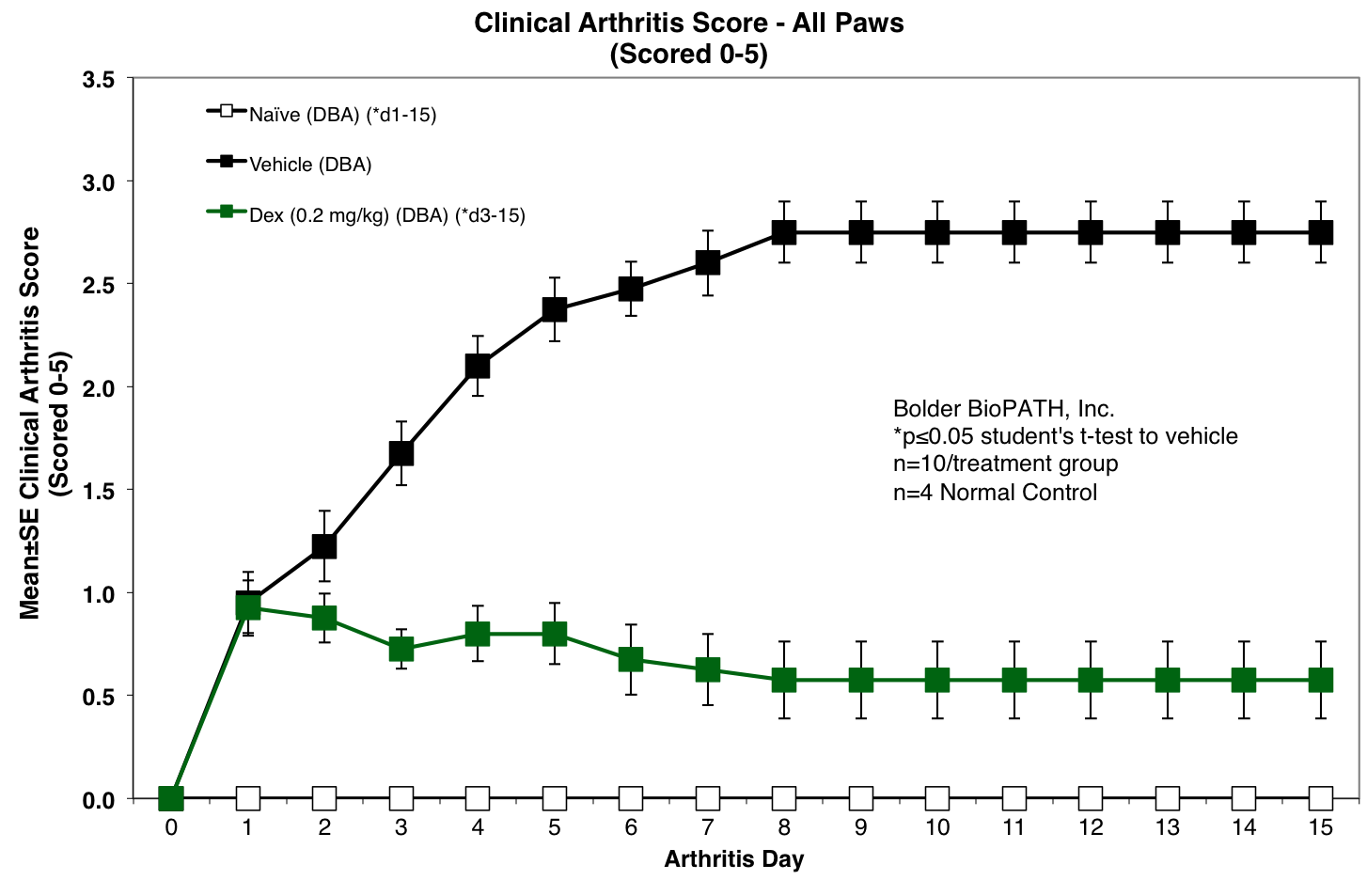
Clinical scores are given for each of the paws (right front, left front, right rear, left rear) on study days 0 through 14.
Clinical Scoring Criteria for Fore and Hind Paws:
- 0 = Normal
- 1 = One hind or fore paw joint affected or minimal diffuse erythema and swelling.
- 2 = Two hind or fore paw joints affected or mild diffuse erythema and swelling.
- 3 = Three hind or fore paw joints affected or moderate diffuse erythema and swelling.
- 4 = Four hind or fore paw joints affected or marked diffuse erythema and swelling.
- 5 = Entire paw affected, severe diffuse erythema and severe swelling, unable to flex digits.
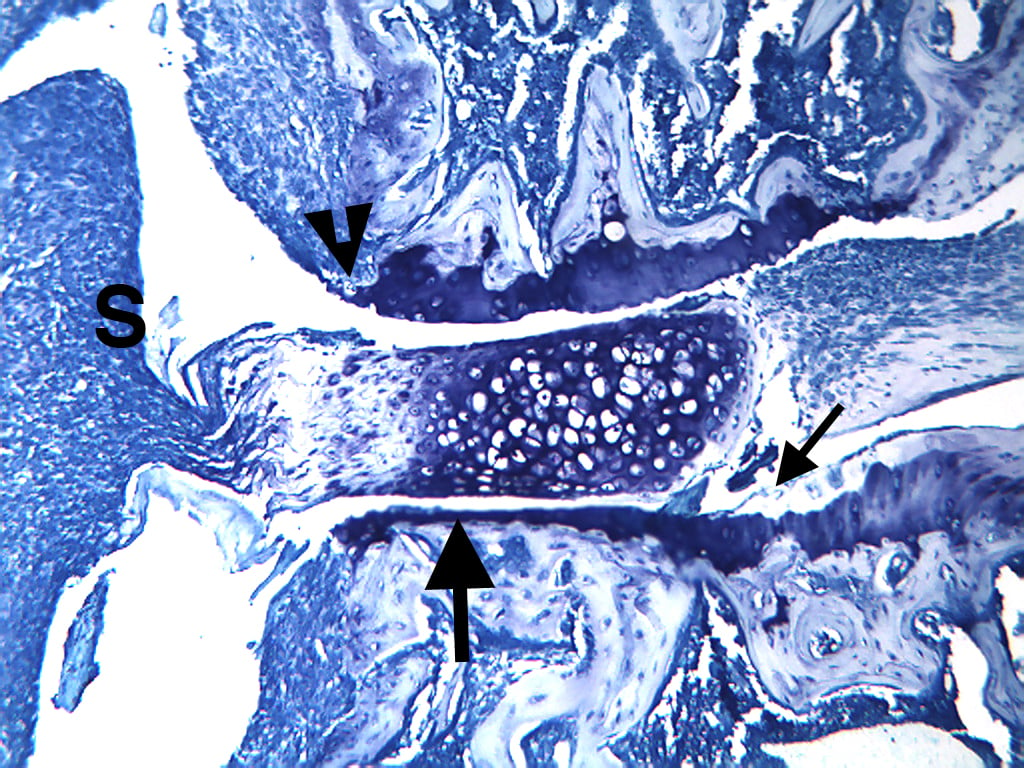
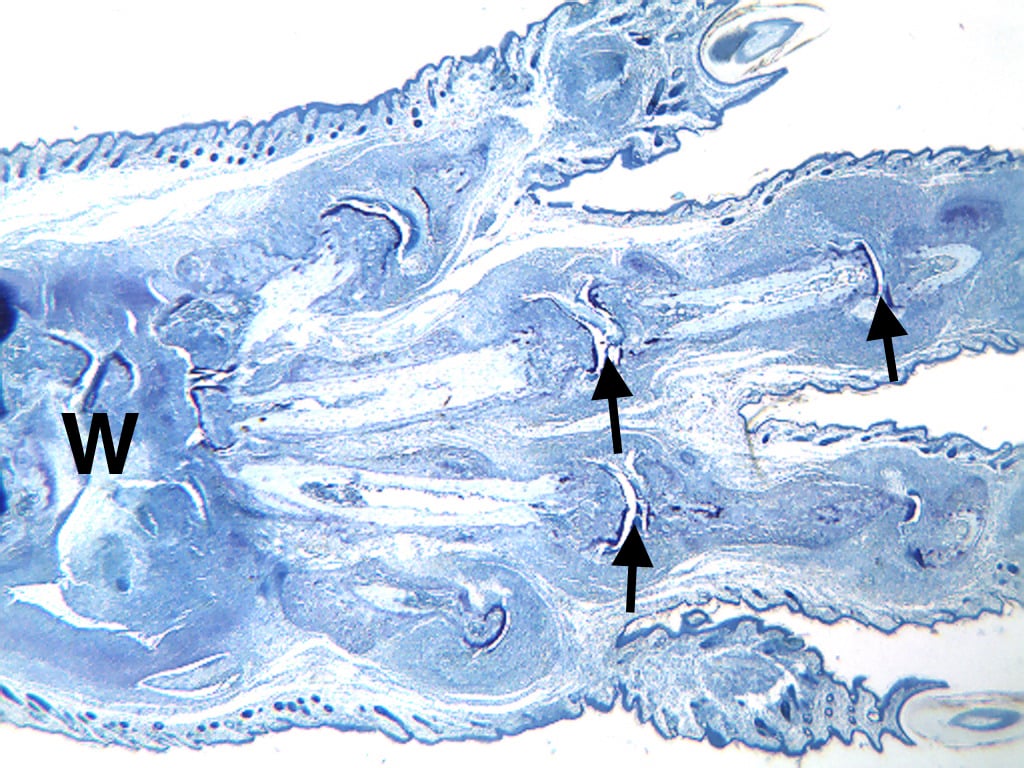
Histopathological Assessment:
Fore paws, hind paws/ankles, and knees are given scores of 0 to 5 for inflammation, pannus formation, cartilage damage, bone resorption, and periosteal new bone formation according to these methods.
Sample Data (click on image to enlarge):
Representative Photomicrographs of Ankle/Knee Joints (14-Day Arthritis)
For additional examples of positive controls, please contact us.
Optional Endpoint:
- PK blood collections
- Knee lavage collection
- Anti-Type II Collagen Antibody ELISA
References
- Terato, K., et al. (1992). Induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to collagen. J Immunol 148(7): 2103–2108.
- Nandakumar KS, Svensson L, Homdahl R (2003). Collagen Type II-Specific Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Mice. Am J Pathol 163(5): 1827–1837.
- Terato, K., et al. (1995). Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice: Synergistic Effect of E. Coli Lipopolysaccharide Bypasses Epitope Specificity in the Induction of Arthritis with Monoclonal Antibodies to Type II Collagen. Autoimmunity 22(3): 137–147.
Referenced Work:
- Chang, B, et al, The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 ameliorates autoimmune arthritis by inhibition of multiple effector cells
- Arthritis Research & Therapy 2011
- Cowden, J. et al, The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and Th17 responses in preclinical models of arthritis
- Ann Rheum Dis 2014
For more information about Antibody Induced Arthritis contact us here.