Oxazolone Induced Ear Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse)

Induction:
On study day 0, mice are sensitized with aliquots of 150 µL of a 5% oxazolone solution epicutaneously on their shaved abdomens. On day 7, the right ear of each mouse is challenged with 3% oxazolone solution (10 µL on the front and 10 µL on the back). Left ears are painted on both sides with an ethanol/acetone mixture.
Disease Parameters/Progression:
Mice develop swelling within 24 to 48 hours of antigen challenge.
Dosing Paradigms:
- Treatment is administered 15 minutes to 1 hour prior to antigen challenge
- Route of administration: SC, PO, IP, IV, topical
Clinical Assessment:
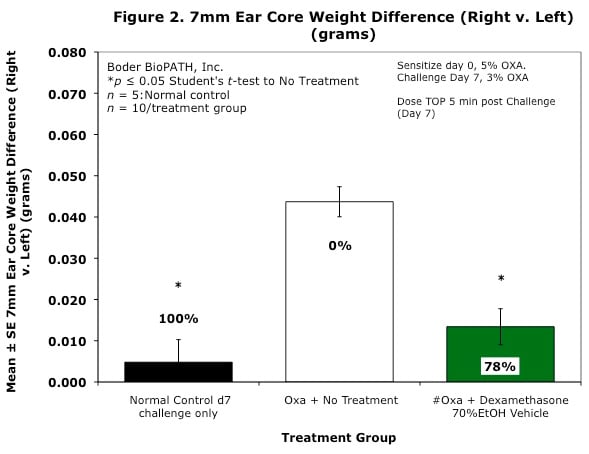
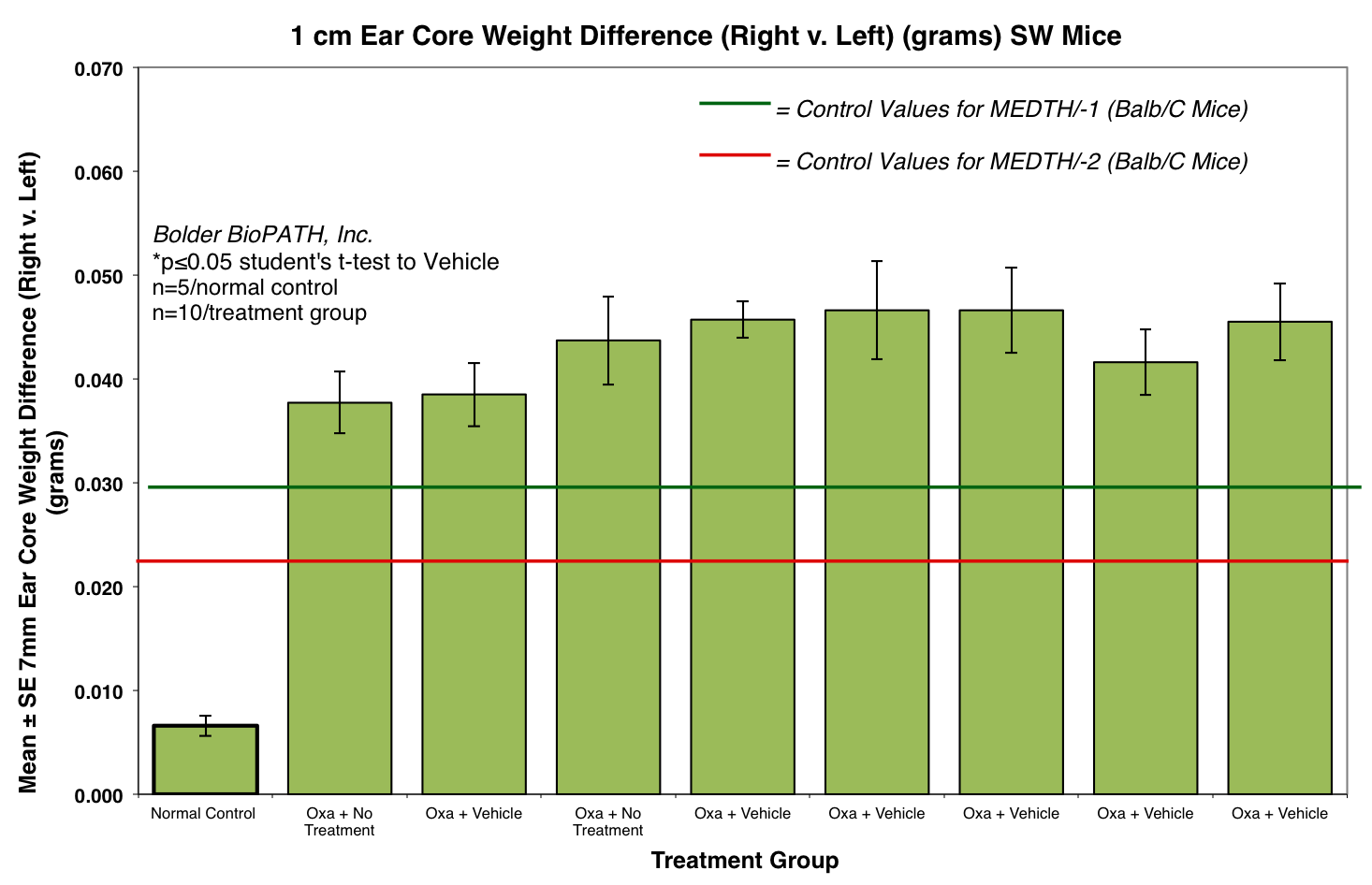
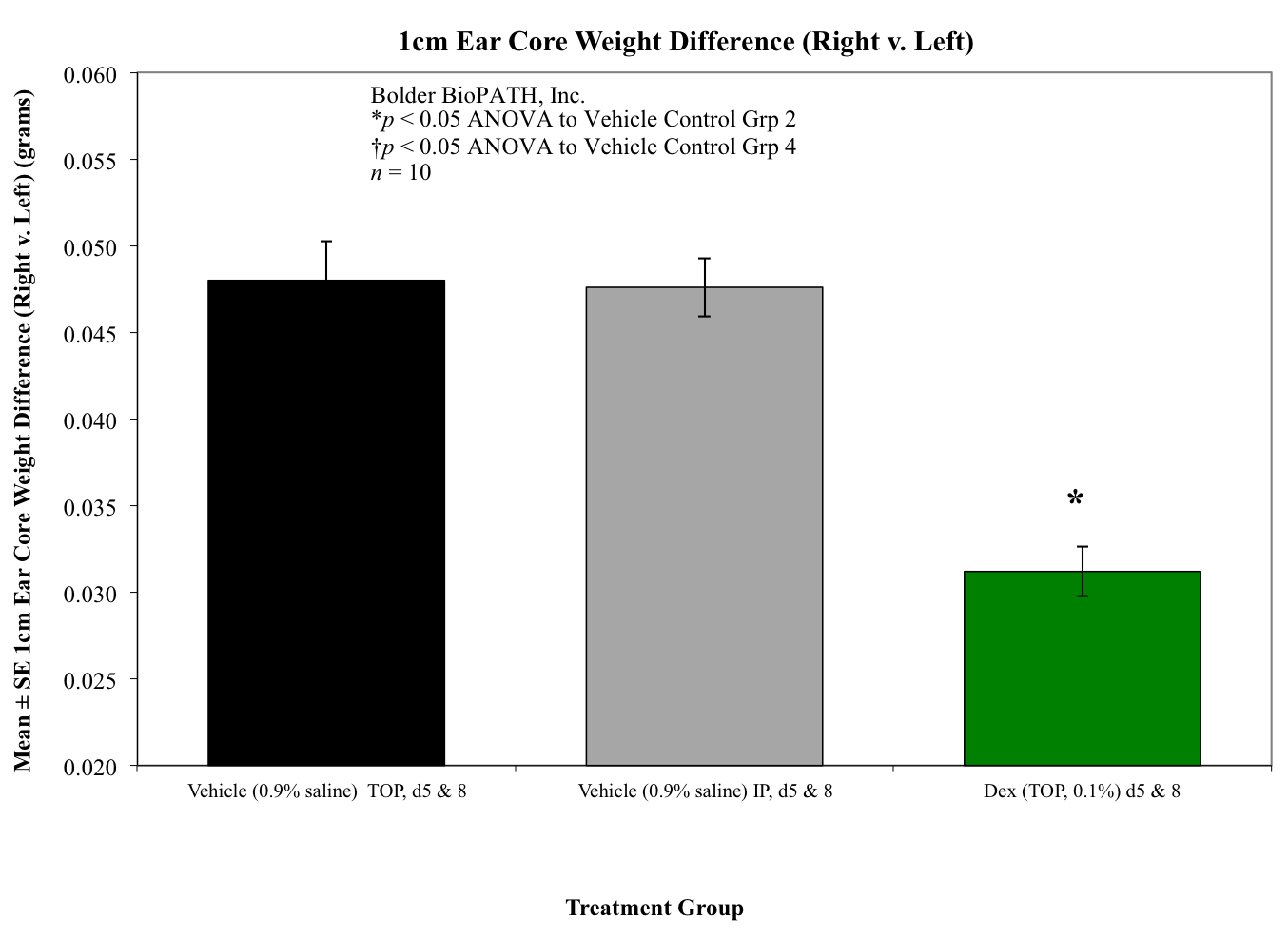
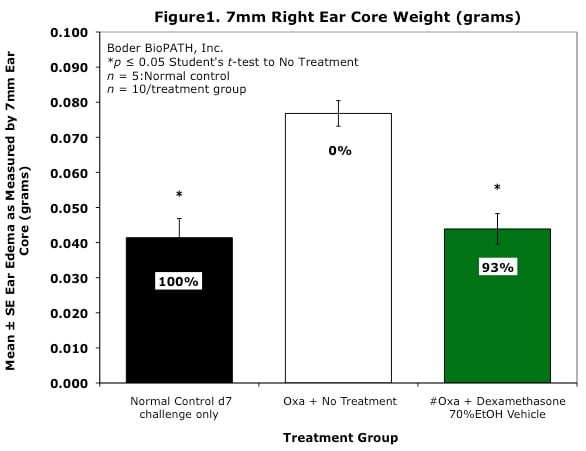
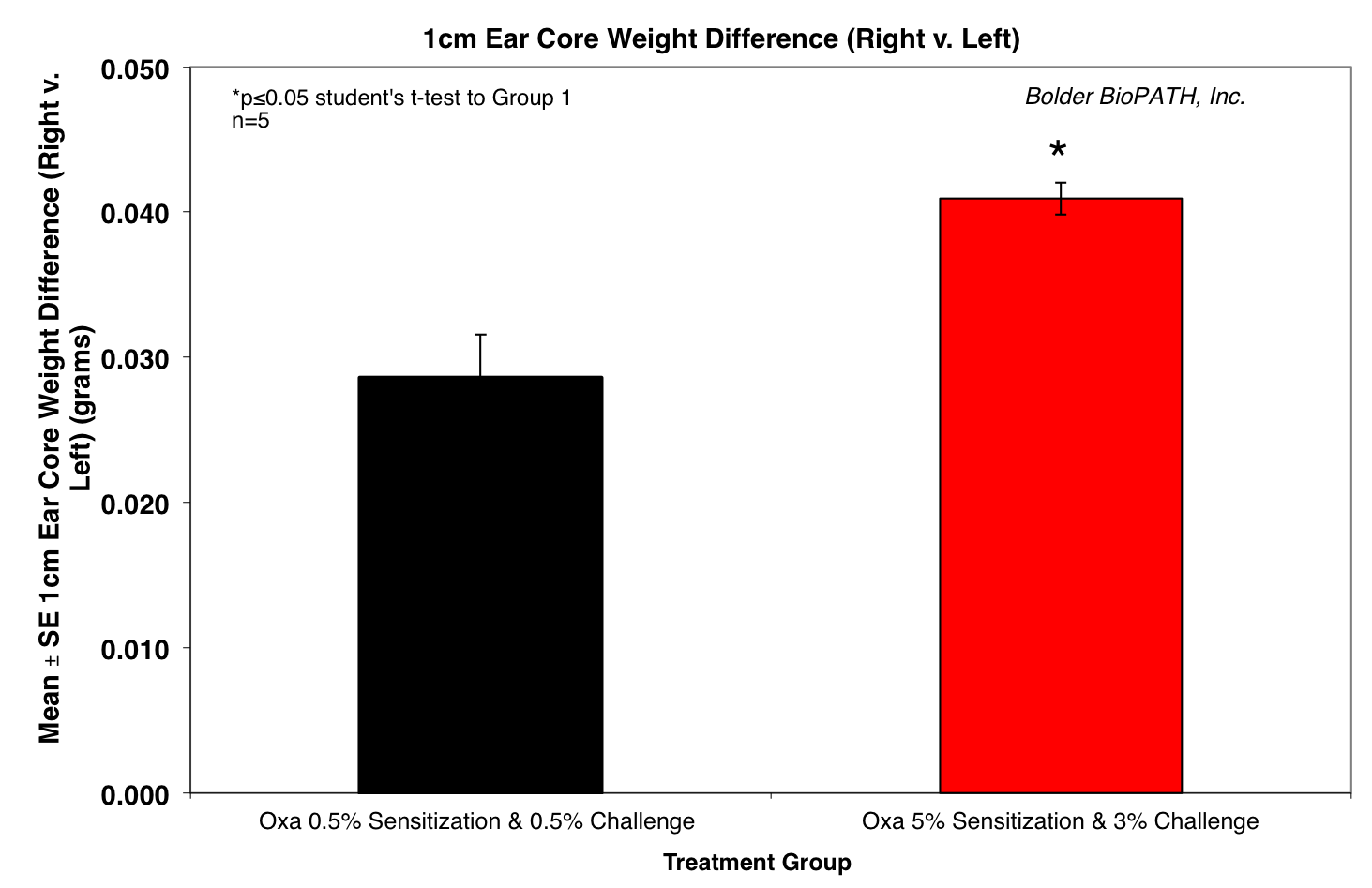
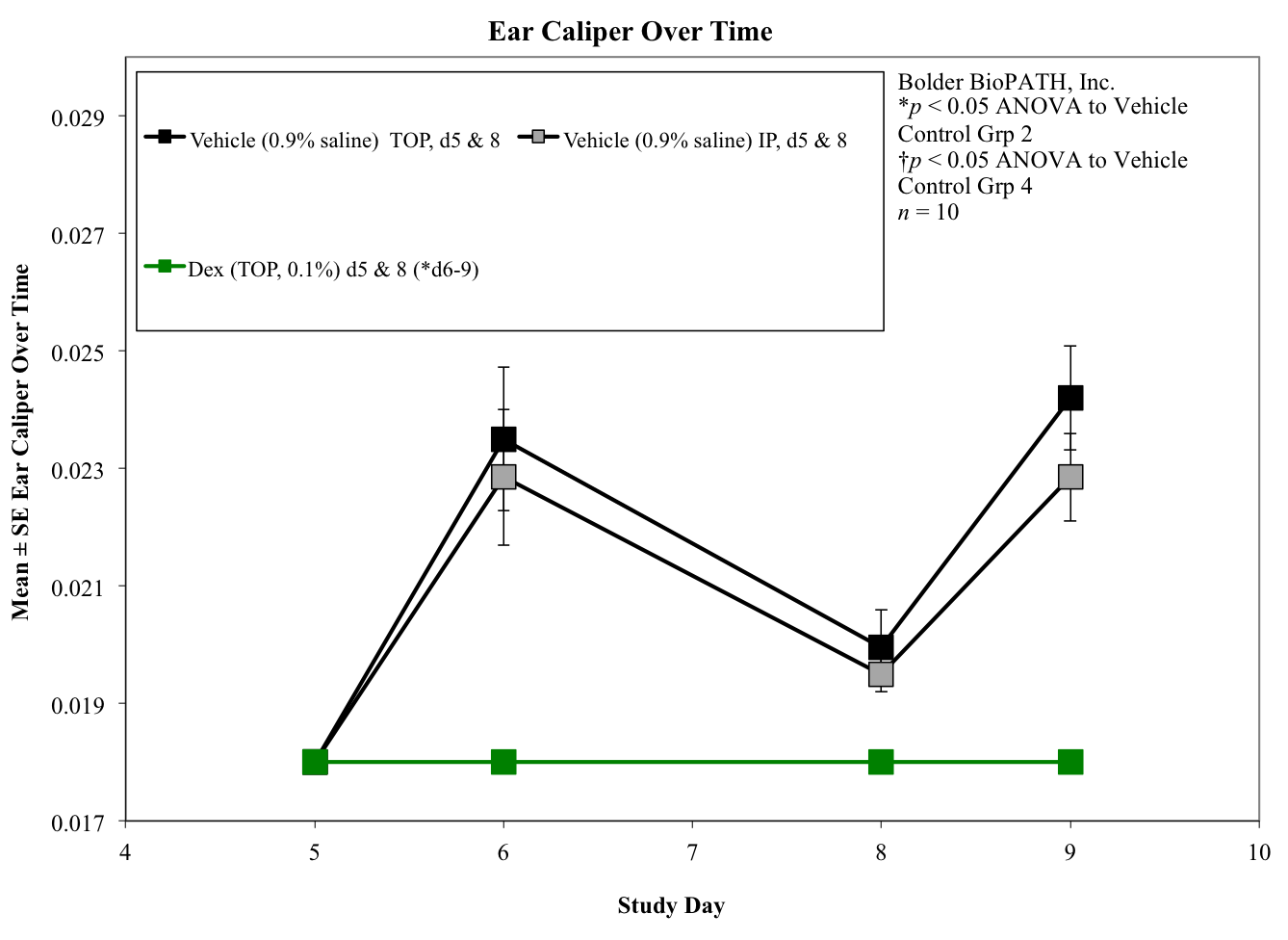
Body weights are taken on study days 0, 7, and 8 (prior to termination). Ear caliper measurements are taken on days 7 (baseline) and 8 using a Digitrix II micrometer (Fowler & NSK). On day 8 (24 hours post-antigen challenge), animals are necropsied. Measurement of the DTH reaction can be done grossly by comparing the ear core weight difference between normal versus antigen-injected ears (weight is proportional to edema). A 7-mm disc is collected by cork borer (Fisher Scientific) from the pinna of each ear and weighed.
Histopathological Assessment:
Tissues are examined microscopically by a board certified veterinary pathologist (Dr. Alison Bendele) and scored according to these methods.
Sample Data (Click on image to enlarge):
For more information about Oxazolone Induced Ear Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse) contact us here.
Notes:
Chemokines such as IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1a (MIP-1a), and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) have been found to be involved in the recruitment of leukocytes to the DTH reaction site. Cytokine inhibitors, such as anti-IL-16, have been shown to minimize the DTH response. Other compounds that effectively inhibit the DTH reaction are dexamethasone (a potent steroid that induces lympholysis) and cyclosporine-A (CsA), which inhibit the action and growth of T-lymphocytes.
Optional Endpoint
- PK/PD blood collections
- Cytokine/chemokine analysis via Luminex(R)
- Other sandwich ELISAs
- CBC/clinical chemistry analysis
- Soft tissue collection
- Histopathologic analysis
- Immunohistochemistry analysis
References
- Yoshimoto T, Wang CR, Yoneto T, et al. Role of IL-16 in delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. Blood. 2000;95(9):2869–2874.
- Owen J, Punt, J, Stranford S. Kuby Immunology. 7th ed. New York: WH Freeman & Company; 2013. Chapter 15, Inflammation: Allergy and Hypersensitivities.
Related Pages
General Inflammation
- Oxazolone Induced Ear Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse)
- mBSA Induced Footpad Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (Mouse)
- Carrageenan Induced Paw Edema (Rat & Mouse)
- Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cytokine Cascade (Rat, Mouse)
- IL-23 induced Psoriasis (Mouse)
- IMQ induced Psoriasis (Rat, Mouse)
- Monosodium Urate-Induced Gout
- Zymosan Induced Peritonitis
- Non-Lethal Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis (Rat, Mouse)