Hepatic Disease & Injury

Fibrotic liver disease is caused by a number of insults including hepatitis, trauma, statins and steroids.
A central process in liver fibrosis is the activation of hepatic stellate cells, ultimately resulting in remodeling and portal hypertension. Several hepatic disease models produce robust hepatic fibrogenesis, which can serve both as a platform for developing hepatic therapeutics and also as a functional screening paradigm for general anti-fibrotic programs.
Hepatic
| Model | Species | Top Tier Data |
|---|---|---|
| Bile Duct Ligation (BDL) Induced Liver Fibrosis | Rat (Mouse – Under Development) |
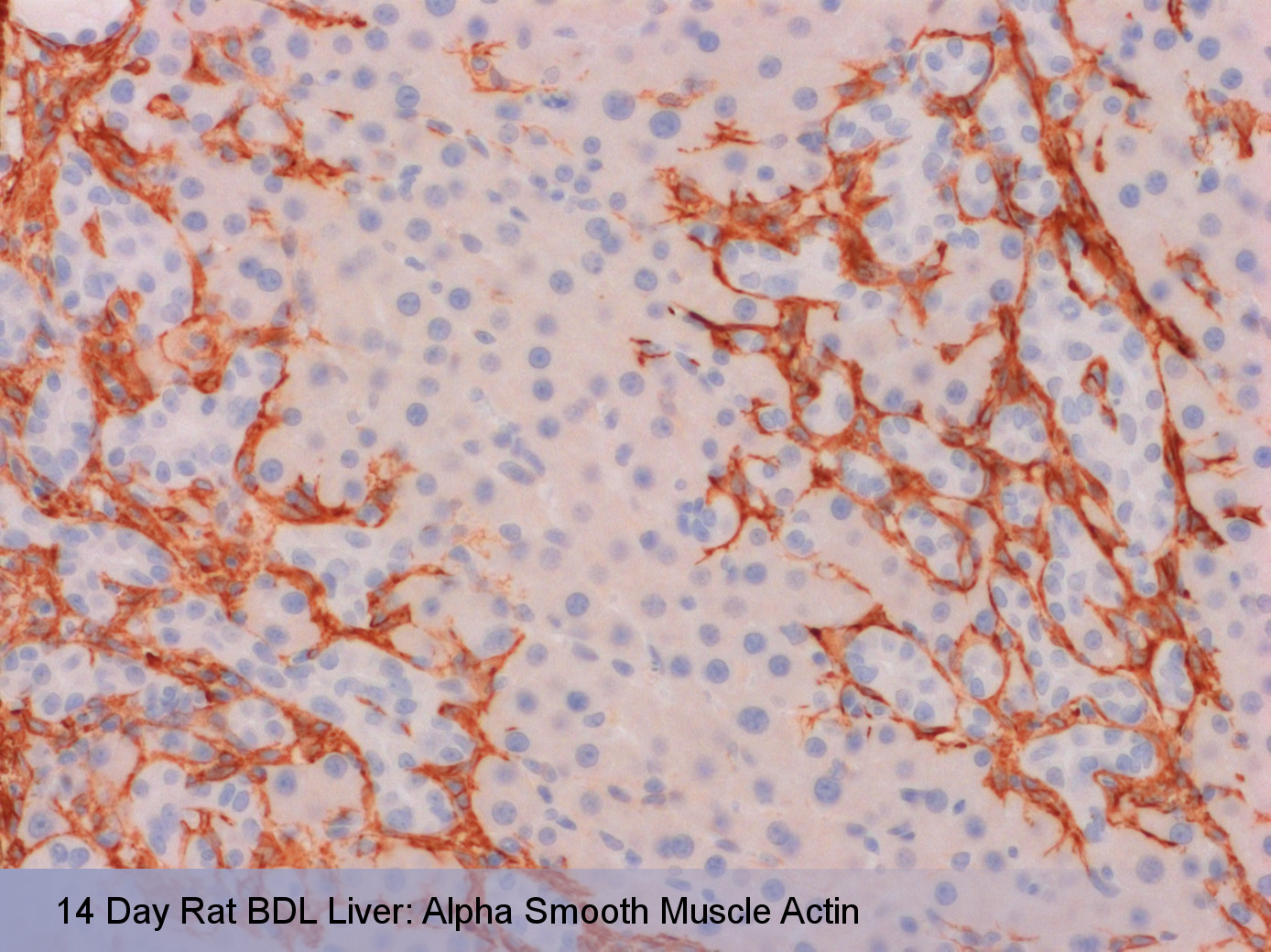
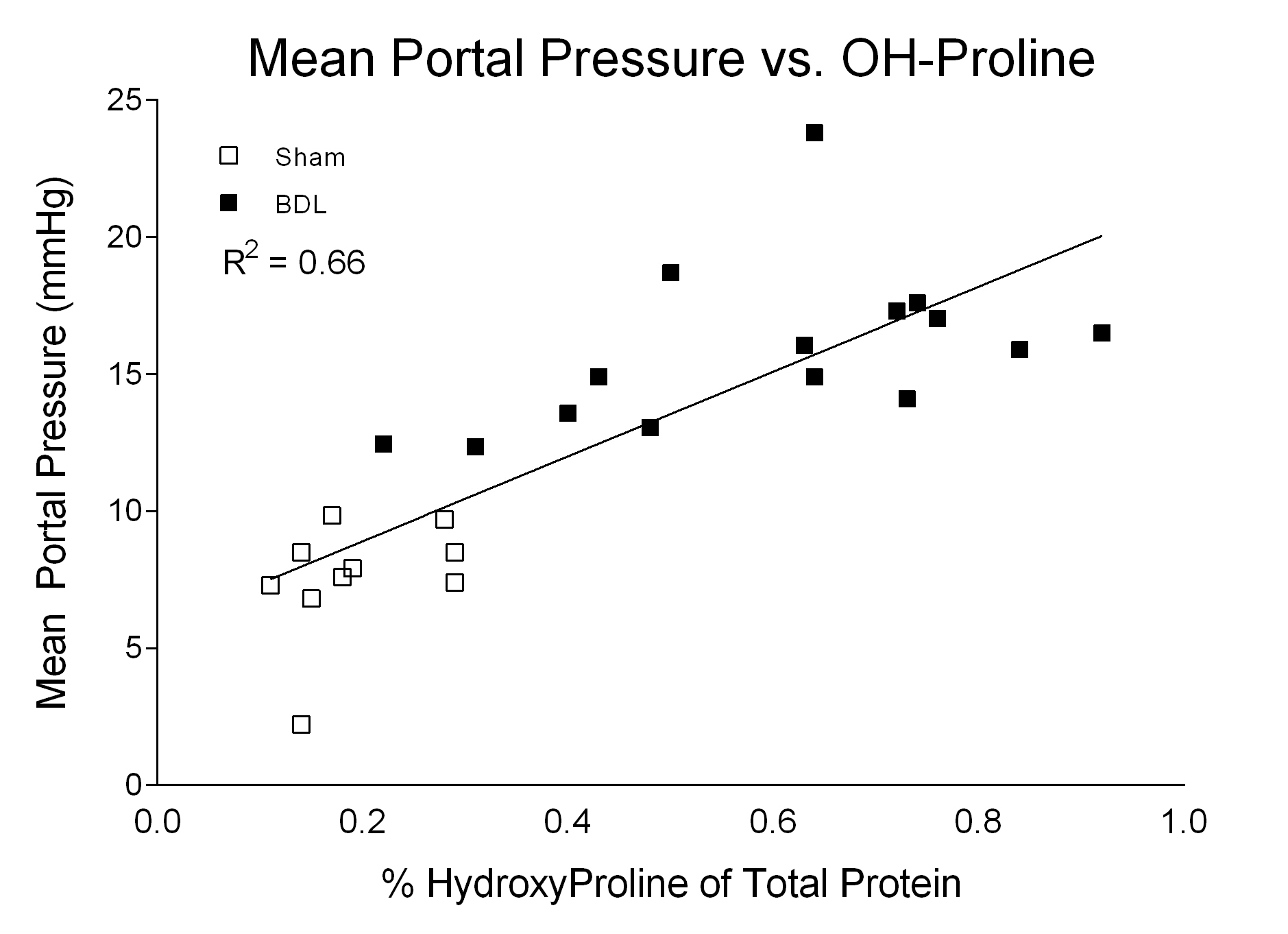
• Mean Portal Pressure (Direct) • Serum AST, ALT, ALP, Bilirubin, Bile Acids, Albumin, Creatinine, BUN • Liver Histology (Fibrosis, macrophage infiltration, α-Smooth Muscle Actin expression) |
| Dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) Induced Liver Fibrosis | Rat | |
| Thioacetamide (TAA) Induced Liver Fibrosis | Rat |
Orthogonal approaches are taken to evaluate models of liver fibrosis. Functional, histological and biochemical measurements, such as Mean Portal Pressure, α-Smooth Muscle Actin and Hydroxyproline respectively, are evaluated to characterize disease severity and therapeutic value.